eCommerce supply chain management covers every step in delivering products to customers. It involves sourcing, warehousing, inventory, fulfillment, shipping, and returns. The process ensures each link works seamlessly toward delivering the right product at the right time.
This system forms the foundation of any online business model. It powers customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and long‑term growth. In today’s world, where shoppers expect fast delivery and flawless service, mastering this chain stands as a competitive edge.
In this article, we will discuss how supply chain management works, as well as its role in the overall eCommerce ecosystem.
Role of eCommerce in Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is an essential part of the overall eCommerce architecture. Not only does it help to establish trust and build loyalty, but it also creates competitive advantages based on advanced technologies and tools.
Increased demand for fast and timely delivery
eCommerce logistics emerges. Businesses must reconfigure systems for same-day or two‑day delivery.
Brands like JD.com have built vertically integrated networks with 900 warehouses and full control from storefront to delivery. This approach helps deliver products faster and more reliably while cutting costs.
For instance, Skechers saw delivery time reduced by around five hours and costs drop 11%, thanks to JD Logistics’ integration of digital forecasting and physical distribution tools.
Increased Price Competition
Online marketplaces amplify pricing pressure. Sellers must streamline logistics costs to stay competitive. They also need to take into account digital demand forecasting, lean inventory strategies, and smart fulfillment.
Optimizing eCommerce supply chain strategy becomes a direct factor in surfacing better pricing and margin control.
New and innovative ways to reach customers
eCommerce opens doors to new models like dropshipping, direct‑to‑consumer storefronts, and marketplace ecosystems. These models let businesses test new markets without large warehousing overhead. Also, they offer agile eCommerce supply chain solutions.
Easier exchange of documents and data
Digital systems eliminate manual paperwork. EDI, cloud platforms, and collaborative tools ensure invoices, orders, and tracking data flow instantly.
That speeds coordination, reduces human error, and strengthens electronic supply chain management systems.
Improved customer experience
Digital platforms collect customer data like preferences, purchase timing, and returns. This data is being analysed via eCommerce logistics & supply chain systems to personalize experiences.
Accurate stock data, real-time updates, and faster delivery build trust and loyalty. Digital commerce intelligence helps optimize pricing, promotions, and even stocking.
eCommerce has a dual function in Supply Chain Management
Retailers act as both buyer (from suppliers) and seller (to customers). Drop‑shipping lets them act as facilitators without inventory holding. This is how they simplify their eCommerce supply chain and reduce overhead.
Greater supply chain visibility and transparency
Visibility helps business owners see every product’s journey. For cheap movers supply chain management, this level of transparency is critical to controlling delivery costs, lead times, and service reliability. Tools like time tracking apps and real‑time monitoring systems offer end-to-end oversight, reducing delays, improving responsiveness, and building customer trust.
Benefits include streamlined inventory, better forecasting, reduced lead times, and faster problem resolution. A Redditor noted:
Smart technology is transforming supply chains by making them more visible, secure, and sustainable… track their supply chains in real.
Expansion into global and cross‑border trade
eCommerce platforms like Amazon’s Global Selling help small sellers export directly. India’s exports reached $5 billion in 2024.
Going global widens markets but adds customs, tariffs, and logistics complexity, demanding smart supply chain strategies.
Data‑driven decision making for better supply chain strategies
Modern SCM relies on analytics. Forecasting, demand trends, returns, and performance data sharpen automated inventory replenishment, warehouse planning, and fulfillment routing.
Tools like CPFR (Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment) align suppliers and retailers, improving efficiency and reducing cost.
Stages of the eCommerce Supply Chain: How it Works
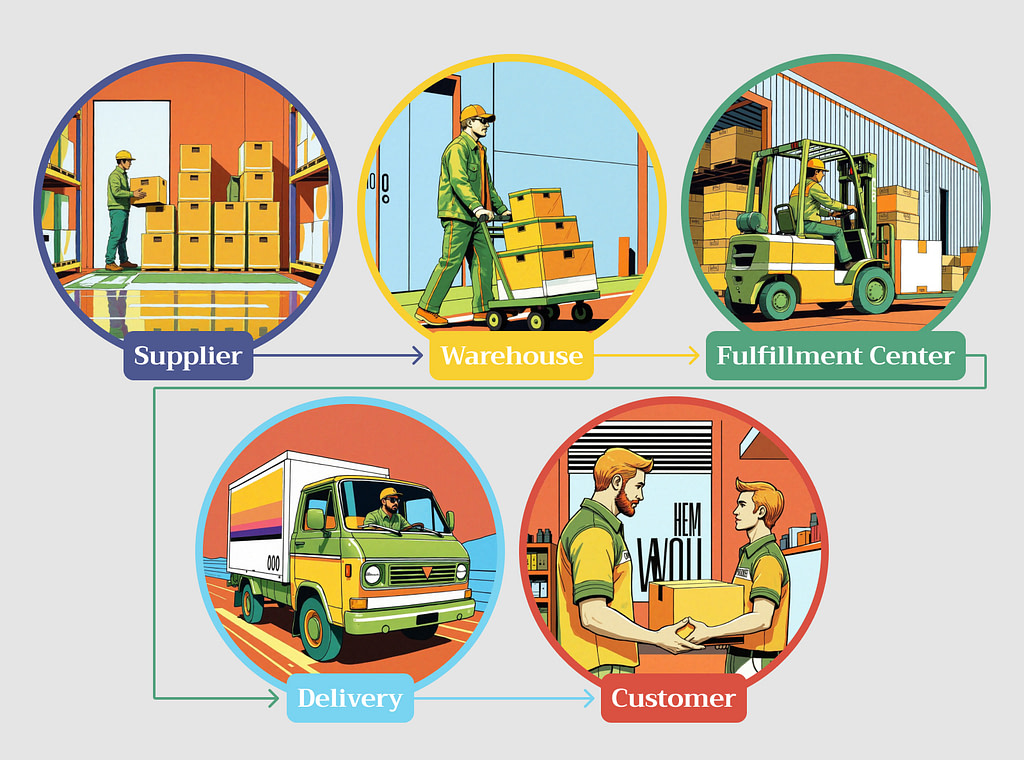
To understand how the entire system works, we need to break it down into fundamental stages.
Suppliers and inbound logistics
This is where collaboration matters. Systems like VMI (Vendor‑Managed Inventory) give suppliers oversight of inventory levels, reducing stockouts and wastage. They are all managed via data sharing and electronic integration.
Warehousing and inventory management
Inventory optimization improves the match between stock and reality. Techniques help choose optimal inventory levels and warehouse locations.
It is the way to balance cost and service. Robotics, as used by Skims and others, speeds up picking and sorting, boosting efficiency and worker support.
Order processing and fulfillment centers
Here, automation shows its strength. OMS systems coordinate orders with stock availability and warehouse operations to ensure accurate packing and fast fulfillment. Machines reduce errors and scale capacity gracefully.
Distribution, delivery, and returns
Distribution becomes strategic. Networks like Amazon or Walmart manage regional hubs, micro-fulfillment centers, or even autonomous delivery methods. Handling returns efficiently becomes another differentiator while streamlined returns reduce cost and bolster customer satisfaction.
Key Challenges in eCommerce Supply Chain
With all that being said, building an efficient supply chain is not easy. There are some crucial challenges entrepreneurs need to consider.
Inventory and warehouse management difficulties
Maintaining optimal stock can be a challenge. Demand spikes, seasonal trends, or unpredictable buying patterns lead to overstock or shortages.
Inventory optimization and analytics are key. Without them, businesses suffer lost sales or waste.
Complexities in transportation and last‑mile delivery
The last mile is costly and operationally complex, especially for small, scattered deliveries.
Tractor Supply tackled this by using their own trucks and drivers to deliver bulky goods in rural markets. It helped them boost satisfaction and repeat orders.
Managing returns and rising customer expectations
Free and easy returns burden logistics. Businesses must streamline reverse logistics: automated return labels, clear inspection processes, and fast refunds keep customers happy and costs contained.
What Strategies Make an E‑Commerce Supply Chain More Effective?
Now, let’s review crucial factors that help to build a sustainable and effective supply chain.
Supply chain efficiency & automation
Automation slashes error rates and speeds operations. AI powers demand forecasting, predictive restocks, and smart routing. As noted on Reddit:
Automation… helps companies save time… minimize human errors…
Warehouse optimization
It can be accomplished with smart layouts, robotics, dynamic slotting, and decentralized warehouses. Efficient configuration cuts pick time, reduces travel inside warehouses, and accelerates fulfillment.
3PL partnerships
Third‑party logistics providers offer scalable warehousing, fulfillment, and delivery. They reduce infrastructure investment, especially when businesses expand or enter new regions.
eCommerce delivery strategies
One can boost flexibility by offering options like standard, express, in-store pickups, click‑and‑collect, etc.
But each option demands precise coordination between warehouses, carriers, and customer expectations.
Data‑driven decision making
To make smarter decisions, businesses need analytics across supply chain stage from procurement to returns.
Decision-makers predict demand, balance stock, choose carriers, and adjust fulfillment zones efficiently.
How Is B2B eCommerce Supply Chain Management Different from B2C?
To apply different models effectively, business owners need to have a clear understanding of how B2B supply chain management models differ from B2C.
Specifics of B2B supply chains vs B2C
B2B operates in bulk, large quantities, and negotiated pricing. A B2B procurement platform is key in managing these complexities, offering features like supplier management, bulk purchasing, and volume-based pricing.
Electronic supply chain management (e‑SCM)
B2B relies on systems integration like ERP, EDI, CPFR. They help to connect procurement, inventory, and sales. Automated invoicing, replenishment, and compliance workflows are standard.
eCommerce value chain in B2B
The focus shifts from speed to precision, volume, and relationships. Visibility, order accuracy, and just-in-time replenishment define success in a B2B eCommerce value chain. Companies also increasingly look to specialized platforms such as intelligent B2B procurement solutions to streamline sourcing, improve supplier diversity, and drive long-term efficiency.
How Do Technology and Innovation Shape eCommerce Supply Chains?
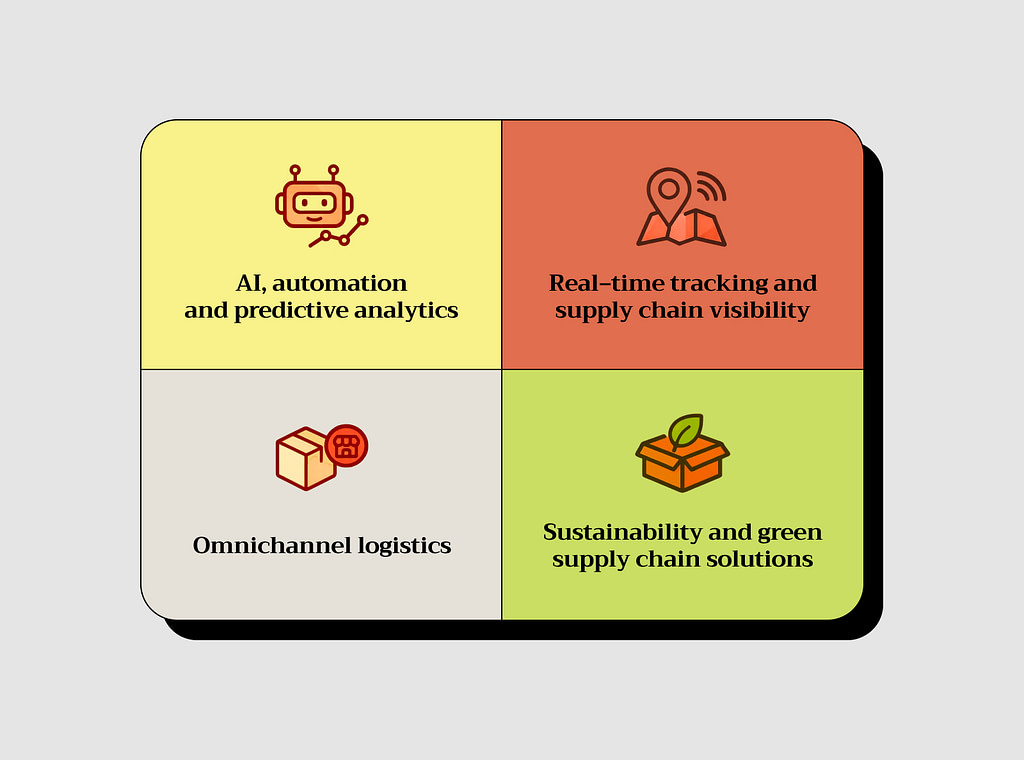
AI and AR-based solutions are shaping the eCommerce industry. New technologies offer dozens of instruments top strategically boost your business.
AI, automation, and predictive analytics
These tools forecast demand, optimize reordering, and support automated picking and routing. AI studies customers’ behaviors, seasonal trends, and even return rates, adjusting operations proactively.
Real‑time tracking and supply chain visibility
Sensors, GPS, RFID, and cloud dashboards bring clarity across global supply chains. They improve collaboration, reduce delays, and fuel trust.
Omnichannel logistics
Customers interact via online, mobile, or physical stores. Stock sync across channels ensures consistent service. The tool requires integration with inventory and fulfillment systems.
Sustainability and green supply chain solutions
Green goals align with tech: JD.com’s Green Stream Initiative cut 50,000 tons of plastic and 1.3 million tons of paper.
IoT sensors, optimized routing, and eco-friendly packaging also reduce environmental impact while appealing to conscious consumers.
Conclusion
eCommerce supply chain management is a dynamic, data-powered ecosystem. From inbound sourcing to final delivery, savvy entrepreneurs use automation, visibility, global systems, and sustainability to build resilient, efficient, and customer‑centric supply chains.
It is important for business owners to embrace the role of eCommerce in supply chain management. Then, leverage it to shape faster deliveries, smart inventory, and stronger customer relationships. That might turn out to be a crucial competitive advantage.