For eCommerce businesses, safety is not just a technical issue. Back in 2024, companies lost around $44 billion because of fraud. Meanwhile, customers expect their data to stay safe. They expect transactions to be secure and experiences to be seamless.
Today’s digital storefronts face threats from all sides: payment fraud, malicious bots, synthetic identities, account takeovers, and insider leaks. This is where the Zero Trust Security Model becomes essential.
Zero Trust helps online retailers lock down sensitive data through continuous security measures without slowing down the shopping experience. This data may include sensitive customer information and payment details. By verifying every user, every device, and every request in real time, Zero Trust stops threats before they can do damage.
In this article, we will take a closer look at how this model works alongside its mechanisms and crucial benefits for business owners.
What Is Zero Trust Security?
The Zero Trust Security Model flips traditional network perimeter-based safety on its head by continuously inspecting and securing network traffic. Instead of assuming everything inside the network is trustworthy, Zero Trust takes the opposite stance and trusts nothing. Instead, it verifies everything. Whether a user connects from inside the office or halfway across the globe, Zero Trust treats every request as potentially fraudulent.
This model responds to a modern reality that says “corporate data lives everywhere”. On laptops, in cloud apps, across hybrid networks. The idea that a firewall can protect it all is outdated. Zero Trust addresses that by shifting focus from network location to user identity, device posture, and context. At its core, the Zero Trust concept is built on the idea that no user or system should be trusted automatically—regardless of location.
In real time, the model helps to:
- Prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, even if login credentials are compromised.
- Handle strong identity checks and continuous monitoring to identify common attack vectors.
- Ensure digital safety policies as your customer base grows and your tech stack expands.
- Let companies meet PCI DSS, GDPR, and other regulatory requirements with consistent access controls and audit-ready logs.
Zero Trust gives eCommerce entrepreneurs the edge without adding friction to the customer journey. It also promotes better cyber hygiene across the organization by enforcing consistent access and behavior standards. A Zero Trust strategy is not just a technical upgrade—it’s a mindset shift that prioritizes verification and access control at every point. Now, let’s get down to its core principles.
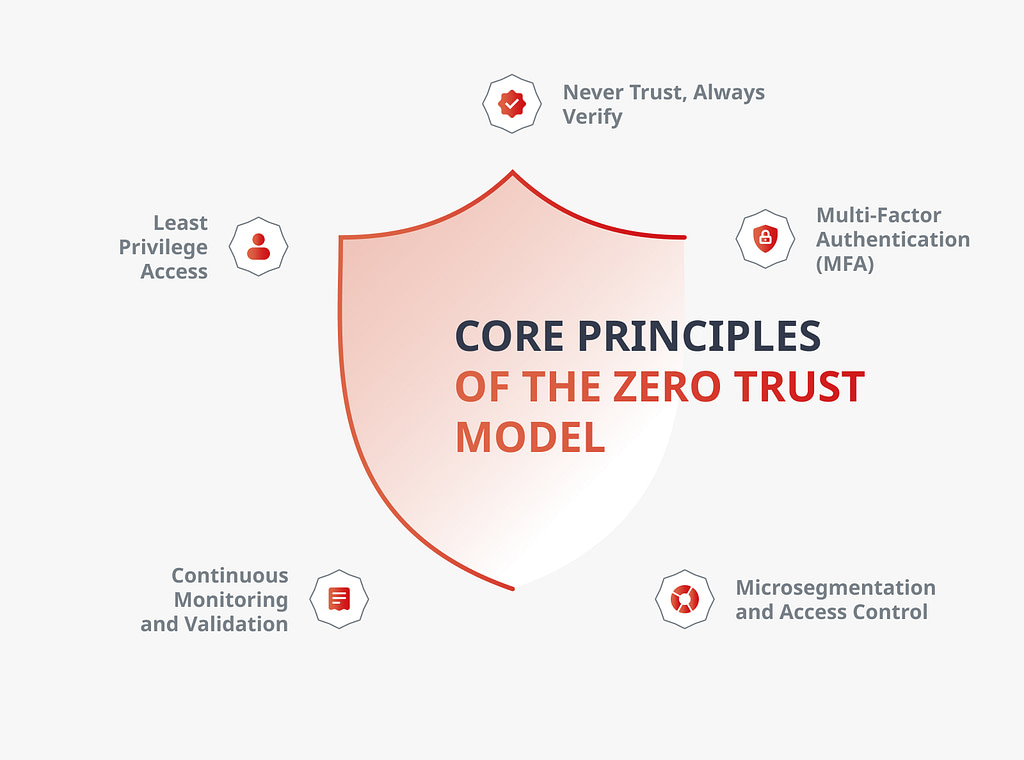
Core Principles of the Zero Trust Model
Before diving into the architecture, it’s important to understand the Zero Trust principles that make the model work. The model is built on a set of core principles that guide every access decision.
These principles replace assumptions with verification and put tight controls around how users and systems interact. One of the foundational ideas behind Zero Trust is the principle of least privilege, which minimizes risk by restricting access rights.
Let’s break them down and see how Zero Trust architecture and security policies bring these principles to life.
Never Trust, Always Verify
Every access request must prove its legitimacy through strict identity verification and continuous risk evaluation. This is the foundation of Zero Trust.
A valid login alone doesn’t earn trust. Users and devices must authenticate continuously and contextually based on behavioral and technical parameters, risk score, location, and other risk-factors.
Any abnormality is actually a red flag that is associated with potential fraud.
Least Privilege Access
Zero Trust limits access to only what is necessary. Even verified users cannot gain access to resources beyond their defined role or privileges. Users can’t roam the network freely. They only get the minimum permissions required for their role. Zero trust access means that every user and device must prove their trustworthiness before receiving even limited permissions.
This dramatically reduces the attack surface, restricts user access, and stops lateral movement in case of compromise or internal data leakage.
Continuous Monitoring and Validation
Digital safety should not be considered as a one-time gate check, but rather a process of continuous verification and risk assessment. Zero Trust systems continuously monitor behavioral patterns looking for anomalies. But proactive defense starts before anomalies appear—use this holiday security checklist to harden your site ahead of seasonal threats. Examples include using obfuscation techniques like randomizers to conceal real identities
If anomalies or mismatches are detected, the system re-evaluates the access immediately.
Microsegmentation and Access Control
Microsegmentation breaks up the network into smaller, isolated zones to enhance security and limit the impact of potential breaches. Unlike traditional network segmentation, which relies on broad perimeter controls, microsegmentation applies fine-grained policies within each zone. Each secure zone enforces its own access rules, preventing lateral movement even if one area is compromised.
Even if a fraudster gets into one area, he will not be able to move to another without facing new checks and controls.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is a requirement, not an option. Zero Trust relies on multiple layers of identity verification. They involve passwords, biometrics, hardware tokens, or push notifications.
Even if one factor is stolen, fraudsters won’t get very far.
How Zero Trust Security Model Works
Let’s take a closer look at how the Zero Trust Security Model works behind the scenes to verify identities, enforce policies, and adapt to threats in real time.
Identity and Device Verification
Zero Trust starts by authenticating both the user and the device. With Zero Trust authentication, user and device identity checks go beyond passwords—incorporating behavioral signals and contextual awareness. Who is trying to connect? From what device? Is it healthy, updated, and compliant? If not, access is denied or restricted automatically.
The main concept lies behind examining technical and behavioral factors. Technical factors include type of device, web browser, screen dimensions, and other parameters. Behavioral parameters include the speed of typing and scrolling, the average time on a page, etc. If the system identifies anomalies, it notifies the risk-assessment team.
Policy Enforcement and Access Management
Policies drive access decisions in real time, granting access only when all conditions are met. They consider crucial parameters that help to understand who the user is, what app or data they are trying to access, where they are coming from, and what risk signals are present. If anything does not align, the system blocks or limits access.
Using Analytics and Threat Intelligence
Zero Trust uses telemetry and threat intelligence to inform decisions. Generally, also known as risk scoring models, they use specific mechanisms to handle behavioral analytics needed to spot suspicious patterns like a user suddenly logging in from multiple countries.
The system adjusts trust dynamically based on risk.
Zero Trust Architecture and Technologies
The model represents a framework supported by Zero Trust technologies and specific tools designed to enforce access control and visibility. To build a strong Zero Trust environment, you need the right architecture in place. Additionally, following secure development standards aligned with Zero Trust principles helps minimize risks during custom development.
Here’s what that looks like, and how it works across modern IT ecosystems.
What Is Zero Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA)?
Zero Trust Network Architecture is the practical framework behind Zero Trust. It provides secure, encrypted access to applications without placing users on the full network.
Unlike VPNs, ZTNA grants application-specific access, minimizing exposure.
Components of a Zero Trust Security System
A well-architected Zero Trust system includes identity providers (IdPs), endpoint detection and response (EDR), endpoint management tools, access gateways, policy engines, monitoring tools, and analytics platforms. Together, they enforce policies and adapt based on risk.
Zero Trust in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Zero Trust is cloud-native by design. It thrives in environments where assets are distributed across SaaS, IaaS, on-prem, and remote endpoints, enabling businesses to connect remote employees securely and efficiently.
Whether data lives in AWS, Azure, or a legacy data center, Zero Trust can consistently protect it.
Benefits of a Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust implementation brings practical, long-term advantages. From better data protection to streamlined operations, here are the key benefits organizations gain by adopting a Zero Trust approach.
Stronger Data Security and Compliance
Zero Trust makes it harder for fraudsters to reach sensitive data by reinforcing network security at every access point. With Zero Trust encryption in place, sensitive information stays secure from unauthorized access, even if attackers bypass the perimeter. Granular access controls help meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS—especially for organizations managing sensitive data science workloads and analytical models.
Compliance audits become easier because every access attempt is logged and verifiable.
Protection Against Insider and Credential-Based Threats
Stolen credentials aren’t enough to breach a Zero Trust system. Lateral movement is blocked. Insider threats are monitored and contained. Even if someone is technically “inside,” they still face strong verification barriers.
Simplified and Scalable Security Operations
Zero Trust replaces a patchwork of legacy controls with a unified policy model. It scales across users, apps, and cloud environments without increasing operational overhead. This scalability helps secure even vulnerable network systems that may have been overlooked in traditional architectures. Pairing that with Snyk alternatives strengthens remediation by flagging risky dependencies and auto-opening fix PRs. Centralized visibility makes it easier for risk-assessment and security teams to detect threats and respond promptly.
Zero Trust Use Cases
The model is not limited to one type of business or industry. Its flexibility makes it a good option for a wide range of environments and business sectors.
Here are some examples of how organizations are putting Zero Trust into action.
Securing Remote and Hybrid Workforces
In remote work scenarios, Zero Trust provides secure, consistent access across home offices, co-working spaces, airports, and everywhere in between, without exposing the broader network.
Zero Trust for SaaS, Cloud, and Multi-Cloud
SaaS and multi-cloud environments create new security gaps. Zero Trust protects data as it moves across these platforms, enforcing strong access controls and minimizing risk without slowing users down.
Government and Critical Infrastructure Applications
Governments and critical infrastructure operators face relentless cyber threats. Zero Trust offers a robust, defensible security model that can be aligned with federal standards like NIST 800-207, providing resilience against nation-state actors and advanced threats.
How to Implement Zero Trust Security
Moving to a Zero Trust model requires a clear plan, the right tools, and alignment with industry standards. Here’s how to get started and build a strategy that fits your organization’s needs.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
- Map your data and assets. Understand what needs protection.
- Define access policies. Base them on roles, devices, and context.
- Verify identities and devices. Use strong MFA and posture checks.
- Segment the network. Isolate workloads and restrict lateral movement.
- Monitor continuously. Use telemetry and analytics to adjust trust levels.
- Test and refine. Zero Trust is a journey, not a switch.
Aligning with NIST 800-207 and Other Standards
The NIST 800-207 framework offers a structured path to Zero Trust. It defines key elements: policy engines, trust algorithms, and decision-making models. Following it helps ensure compliance and interoperability.
Choosing the Right Zero Trust Security Solutions
There is no one-size-fits-all platform. Today’s vendors offer a wide range of Zero Trust security solutions tailored for different business sizes and industries. Choose tools that integrate well with your identity systems, cloud services, and endpoint solutions. If you use CS-Cart or Multi-Vendor, follow this hands-on security guide to ensure your platform is properly configured for Zero Trust principles. Prioritize vendors that support open standards and provide strong visibility into user behavior.
Conclusion
Fraudulent patterns constantly evolve. Fraudsters keep developing new schemes. For companies, it means trusting users by default is no longer an option. By verifying everything, limiting access, and enforcing policies intelligently, Zero Trust creates a safer, more agile foundation for modern companies.
It takes planning, but the payoff is huge: fewer breaches, tighter compliance, and security that scales with your organization. By building a consistent Zero Trust security posture, companies can stay resilient in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Would you like to migrate to the Zero Trust Security Model?

