Marketplaces are not limited to physical products. The information age has brought its own specific ways of trading. As markets have gone digital, so has data trading. Today, data marketplaces have become one of the most valuable commodities, fueling industries and driving innovation.
Data is often referred to as the new oil, and businesses that know how to leverage it gain a significant competitive advantage. Did you know that the global data economy is projected to reach $550 billion in 2025? However, buying and selling data securely remains a challenge. Today, we’ll explore this topic by examining some of the best platforms that simplify and streamline data trading.
What is a Data Marketplace?
A data marketplace is a platform where data providers (sellers) and data consumers (buyers) can buy, sell, and exchange data securely. These platforms facilitate the sale and purchase of structured and unstructured data while ensuring compliance with relevant regulations while maintaining privacy. By offering a centralized space for data transactions, data marketplaces help bridge the gap between data owners and those in need of valuable insights, such as businesses, researchers, and developers.
What is a data marketplace for organizations across industries? From healthcare and finance to marketing and artificial intelligence, they rely on data marketplaces to gain a competitive edge. These marketplaces serve as intermediaries that streamline data access, making it easier for businesses to find high-quality, relevant, and legally sourced datasets.
Unlike traditional methods of data acquisition, which often involve lengthy negotiations and complex agreements, data marketplace platforms provide an efficient and transparent way to buy and sell data online. Whether you’re looking for real-time market trends, AI sales training, or customer behavior insights, a global data marketplace can help you access a vast range of datasets in just a few clicks.
Additionally, business intelligence marketplaces enable organizations to enhance decision-making through data-driven insights. These platforms often incorporate advanced analytics, AI-powered recommendations, and automated data integration tools to maximize the value of purchased data.
Key differentiators of a data marketplace include:
- Transparency in data sources and pricing, allowing buyers to make informed decisions.
- Secure transactions, ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
- Tools for analyzing and integrating data, helping businesses seamlessly incorporate external data into their existing workflows.
- Diverse data offerings, covering various industries, use cases, and formats.
- Scalability, allowing businesses to access data as needed without the constraints of traditional licensing models.
Now that we understand what data marketplaces are, let’s see how they function.
How Data Marketplaces Work
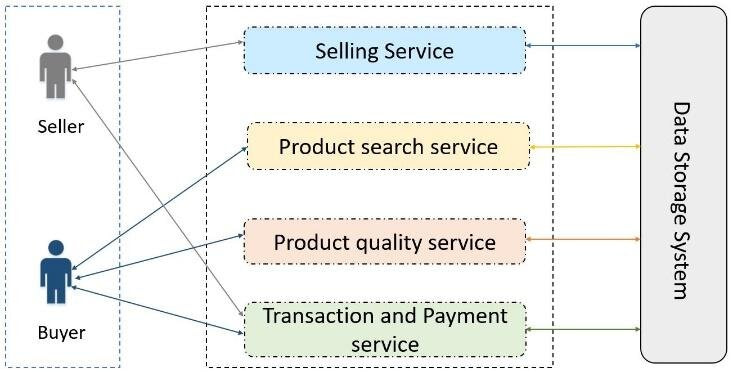
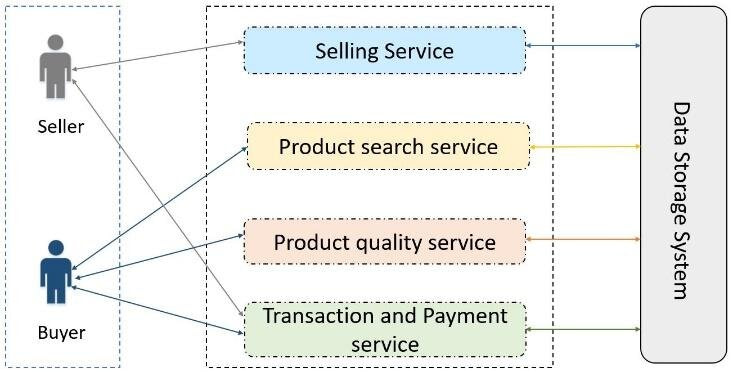
Architecture structure of data marketplace. Source: ResearchGate
Data marketplaces operate much like traditional eCommerce platforms but are specifically designed for data exchange. Here’s how they typically work:
Data Listing
Sellers upload datasets to the marketplace, often including metadata to describe the content, format, and potential use cases. The data is categorized based on industry, data type, and licensing terms, ensuring discoverability.
Data Search and Discovery
Buyers use search tools and filters to find relevant datasets based on keywords, industries, or specific needs. Advanced platforms incorporate AI-driven recommendations and machine learning algorithms to match buyers with the most relevant datasets.
Data Validation and Preview
Many marketplaces offer sample data previews so buyers can assess quality before purchase. Some platforms also validate and certify data to ensure reliability.
Data Transactions
Buyers purchase access to the data, often under specific licensing terms. Payments can be made via subscription models, pay-per-use, or one-time purchases. Some data marketplaces use blockchain-based smart contracts to automate and secure transactions.
Delivery and Integration
Data is delivered through APIs, direct downloads, or cloud-based platforms, enabling buyers to seamlessly integrate it into their existing systems. Some marketplaces provide tools for automated data ingestion and processing, making it easier to incorporate purchased data into business intelligence workflows.
Ongoing Data Management
Buyers can often subscribe to data updates, ensuring they always have the latest information. Some platforms offer automated alerts, real-time streaming data, and AI-powered analytics to help businesses stay ahead of trends.
Data Marketplace vs. Data Exchange
While both data marketplaces and data exchanges involve the buying and selling of data, they are not identical in structure or purpose.
Data Marketplaces
Data marketplaces operate on an open-access model, allowing a broad range of buyers and sellers to participate. They offer a diverse selection of datasets, including consumer behavior insights, financial data, healthcare statistics, and AI training datasets. Transactions on an enterprise data marketplace are typically one-time purchases, subscriptions, or pay-per-use agreements. These platforms emphasize accessibility, scalability, and ease of integration, making them an ideal choice for businesses seeking ready-to-use data.
Data Exchanges
Data exchanges, on the other hand, are often designed for private, controlled environments where data sharing occurs between specific organizations or partners. These platforms focus on data collaboration rather than outright transactions. For example, in a financial data exchange, participating institutions may contribute anonymized transaction data to enhance industry-wide fraud detection. Unlike marketplaces, exchanges may enforce stricter governance policies, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and security protocols.
Comparison of Data Marketplaces and Data Exchanges
| Feature | Data Marketplace | Data Exchange |
| Accessibility | Open to multiple buyers and sellers | Restricted to specific participants |
| Data Ownership | Data is sold, licensed, or leased | Data is shared with controlled access |
| Transaction Model | Purchase-based, subscription, or pay-per-use | Collaborative data sharing agreements |
| Regulatory Compliance | Compliant with general data privacy laws | Often stricter compliance and security measures |
| Use Case | AI training, business intelligence, marketing insights | Industry collaborations, research, internal data sharing |
Some well-known data marketplaces, such as Snowflake Data Marketplace (see the cost of Snowflake here) and AWS Data Marketplace, also incorporate data exchange functionalities, allowing users to both buy and share data seamlessly.
Types of Data Marketplaces
Data marketplaces can be categorized based on their ownership models, the types of data they offer, and their business models:
Public vs. Private Data Marketplaces
Public Data Marketplaces: These platforms are open to any buyer and seller, allowing businesses, researchers, and individuals to exchange data freely. They provide a diverse range of datasets, including demographic data, financial reports, and market research insights. Examples: AWS Data Marketplace, Google Data Marketplace, Snowflake Data Marketplace.
Private Data Marketplaces: These are closed ecosystems where only authorized participants can buy and sell data. Typically used by enterprises, government agencies, or industry-specific groups, they ensure stricter control over data sharing and compliance. Examples: Banking and healthcare industry data exchanges, proprietary corporate data platforms.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Data Marketplaces
Centralized Data Marketplaces: Operated by a single entity, these platforms act as intermediaries, managing transactions and enforcing data quality standards. They often provide additional services such as analytics, compliance verification, and customer support. Examples: Oracle Data Marketplace, Collibra Data Marketplace.
Decentralized Data Marketplaces: Built on blockchain technology, these platforms allow peer-to-peer data transactions without intermediaries. They enhance security, privacy, and transparency while enabling data monetization through smart contracts. Examples: Ocean Protocol, Datum, Streamr.
Read more: How Can You Create An NFT Marketplace in 2024: Comprehensive Guide
Industry-Specific vs. General Data Marketplaces
Industry-Specific Data Marketplaces: These platforms focus on a particular sector, offering highly specialized datasets that cater to industry needs.
- Healthcare: AI-powered diagnostic datasets, patient records, and pharmaceutical research. Examples: Flatiron.
- Finance: Trading data, risk analysis reports, and credit scoring models. Examples: Bloomberg Terminal.
- Retail & Marketing: Consumer behavior insights, customer segmentation data, and advertising analytics. Examples: Adverity.
- IoT & Smart Cities: Sensor data from connected devices, weather tracking information, and energy consumption metrics.
General-Purpose Data Marketplaces: These platforms provide datasets across multiple industries, catering to a broad audience. Businesses, researchers, and AI developers can find data for diverse use cases, from business intelligence to machine learning. Examples: Databricks Data Marketplace, Google Data Marketplace.
Free vs. Paid Data Marketplaces
Free/Open Data Marketplaces: These platforms provide free access to datasets, often funded by governments, non-profits, or research institutions. Open data marketplaces are essential for fostering innovation and public research. Examples: EU Open Data Portal, World Bank Open Data, Data.gov.
Paid Data Marketplaces: These operate on a commercial model, where buyers purchase data under licensing agreements. Pricing structures can include one-time purchases, subscriptions, or pay-per-use models. Examples: Amazon Data Marketplace, Oracle Data Marketplace.
Comparison of Data Marketplace Types
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Public vs. Private | Public: Open to all buyers and sellers, offering diverse datasets. Private: Operates in a closed ecosystem, often industry-specific. | Public: AWS, Google, Snowflake Data Marketplace Private: Banking & healthcare exchanges, corporate platforms |
| Centralized vs. Decentralized | Centralized: Managed by a single entity regulating transactions. Decentralized: Uses blockchain for peer-to-peer data exchange. | Centralized: Oracle, Collibra Data Marketplace Decentralized: Ocean Protocol, Datum, Streamr |
| Industry-Specific vs. General | Industry-Specific: Focuses on particular sectors with specialized datasets. General-Purpose: Offers datasets across multiple industries. | Industry-Specific: Flatiron (healthcare), Bloomberg Terminal (finance), Adverity (marketing) General-Purpose: Databricks, Google Data Marketplace |
| Free vs. Paid | Free/Open: Provides datasets for free, often funded by governments or nonprofits. Paid: Sells data under various licensing models. | Free/Open: EU Open Data Portal, World Bank Open Data, Data.gov Paid: Amazon, Oracle Data Marketplace |
Benefits of Data Marketplaces
Engaging with a data marketplace platform offers several benefits. These benefits extend to businesses, data providers, researchers, and even individuals looking to leverage data for insights and innovation.
Access to High-Quality, Verified Data
One of the biggest challenges businesses face is obtaining reliable and accurate data. Data marketplaces curate and verify datasets, ensuring that buyers receive high-quality, up-to-date information. Many platforms implement quality assurance measures such as:
- Data validation and certification processes to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Standardized metadata and descriptions to help buyers understand the dataset’s relevance.
- Customer reviews and ratings to provide transparency on dataset usability.
Faster and More Efficient Data Acquisition
Traditionally, businesses had to spend weeks or months sourcing data through direct negotiations, partnerships, or expensive research firms. Data marketplaces streamline this process by providing a one-stop-shop for data acquisition, reducing time-to-market. Key efficiency factors include:
- Instant access to datasets instead of lengthy negotiations.
- Advanced search and filtering tools to find relevant data quickly.
- Pre-built integrations with analytics platforms for seamless use.
Monetization Opportunities for Data Providers
Organizations and individuals sitting on valuable data assets can leverage data marketplace solutions to generate new revenue streams. Instead of storing unused datasets, companies can sell anonymized, aggregated, or proprietary data to buyers who need it. Benefits for data providers include:
- Flexible pricing models (one-time purchase, subscription, pay-per-use).
- Global reach, allowing access to a broad customer base.
- Automated licensing and royalty payments through smart contracts on blockchain-based marketplaces.
Cost-Effective Alternative to In-House Data Collection
Gathering first-party data through research, surveys, and proprietary tracking systems is expensive and time-consuming. Data marketplaces provide a cost-effective alternative by allowing companies to purchase pre-collected, structured data instead of investing in expensive data collection infrastructures. Cost benefits include:
- Lower operational costs compared to in-house data gathering.
- Flexible purchasing models that allow businesses to pay only for the data they need.
- Scalability, meaning businesses can start small and scale their data acquisition as needed.
Support for AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML models require vast amounts of high-quality, structured data to improve their accuracy and performance. Data marketplaces support AI development by providing:
- Diverse training datasets, including images, text, speech, and sensor data.
- Labelled and annotated data for supervised learning models.
- On-demand access to real-time streaming data for AI-powered applications.
Read more: 25 Best AI Marketing Tools in 2024
Transparency and Fair Pricing
Traditional data acquisition methods often suffer from opaque pricing models and hidden costs. Data marketplaces solve this by offering:
- Clear pricing structures based on usage, licensing, and dataset type.
- Real-time price comparisons across multiple vendors.
- Performance-based pricing, allowing businesses to pay based on the quality and relevance of data.
Read more: Secure Development Standards in eCommerce
Innovation and Collaboration
Data marketplaces foster innovation by enabling cross-industry collaboration and access to previously inaccessible datasets. Benefits include:
- Startups gaining access to enterprise-grade data for product development.
- Researchers and universities obtaining real-world datasets for academic studies (as an alternative to, e.g., extracting research data from Google Scholar).
- Companies sharing anonymized data to drive collective advancements in AI, healthcare, and sustainability.
| How businesses use data marketplaces | |
| Amazon & Real-Time Supply Chain Data | Amazon leverages supply chain data from third-party providers to optimize inventory management, predict demand fluctuations, and improve delivery speed. |
| Procter & Gamble & Consumer Insights | Procter & Gamble (P&G) uses data marketplaces like NielsenIQ to access consumer purchasing data across various regions. This helps them refine marketing strategies, optimize product placement, and predict emerging trends. |
| JPMorgan Chase & Alternative Data | JPMorgan Chase acquires alternative datasets from financial data marketplaces, such as Bloomberg Terminal, to analyze market trends, assess credit risks, and develop predictive models for investment decisions. |
| Netflix & Recommendation Systems | Netflix integrates external data sources, including content popularity metrics from data marketplaces, to refine its recommendation algorithms. |
| Tesla & Autonomous Vehicles | Tesla uses third-party data sources, including geospatial and weather data from marketplaces, to improve its self-driving algorithms. |
| Pfizer & Clinical Trial Data | Pfizer utilizes healthcare data marketplaces to access anonymized patient data for drug development and clinical trials. |
Challenges & Risks of Data Marketplaces
Despite their advantages, data marketplaces come with several challenges and risks that businesses must consider:
- Data Privacy & Compliance – Regulations like GDPR and CCPA impose strict rules on data handling. Unauthorized data sales or misuse can lead to legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Data Quality & Reliability – Some datasets may be outdated, inaccurate, or biased, leading to flawed insights and poor decision-making.
- Security Risks – Cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access pose significant threats, requiring strong encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information.
- Pricing Transparency & Fairness – Some data sellers may overprice datasets, lack clear licensing agreements, or impose hidden fees, making transactions complex and less trustworthy.
- Ethical Concerns – The misuse of personal data, lack of user consent, and unethical data collection practices raise concerns about privacy violations and corporate responsibility.
Data marketplace examples
Let’s sort out what is what and who is who on the data marketplace by the example of the top data marketplaces operating globally, providing diverse datasets across industries. Prominent data marketplace examples include:
Snowflake Data Marketplace


A cloud-based platform that enables businesses to discover and share live data. It provides seamless access to third-party datasets without the need for complex ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, making data integration easier for enterprises. For end-to-end deployment and optimization, many organizations seek consideration from Snowflake implementation partners.
AWS Data Marketplace


Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a robust data marketplace where users can subscribe to and integrate various datasets into their AWS environments. It supports multiple industries, including finance, healthcare, and artificial intelligence, offering real-time and batch data access.
Focused on consumer insights, eCommerce trends, and retail analytics, Amazon data marketplace enables businesses to purchase valuable data for competitive analysis, demand forecasting, and customer behavior modeling.
Google Cloud Marketplace


Integrated with Google Cloud, this Google data marketplace provides businesses with access to data sets that support big data analytics, AI development, and business intelligence applications.
Databricks Data Marketplace


Designed for AI and machine learning applications, this data market provides high-quality datasets specifically curated for data science projects. It is widely used by organizations looking to build predictive models and automate decision-making.
Collibra Data Marketplace


A governance-focused data marketplace that ensures compliance with data privacy regulations. It helps businesses manage data access while maintaining security and regulatory compliance.
Oracle Cloud Marketplace


Oracle data marketplace is a leading provider of third-party data for digital marketing and analytics. It helps businesses enhance their customer segmentation strategies by providing detailed consumer insights.
ZoomInfo


ZoomInfo is a leading B2B data marketplace that provides businesses with access to accurate and up-to-date company and contact data. It specializes in sales intelligence, lead generation, and market insights, helping businesses identify potential customers, personalize outreach, and drive revenue.
BurstIQ


BurstIQ is a blockchain-powered health data marketplace that enables healthcare organizations, researchers, and businesses to buy, sell, and share health-related data while maintaining strict privacy controls. Using blockchain technology, BurstIQ creates an immutable record of transactions, preventing unauthorized modifications and ensuring data integrity.
These platforms exemplify the growing role of data marketplaces in the global data economy. Here you can read more about Insurance Marketplaces.
Read more:
- Why Build a Service Marketplace: Advantages and Best Practices
- 5 Best Enterprise eCommerce Platforms 2024
- A Complete Guide to B2B eCommerce Development
How to Buy and Sell Data on a Data Marketplace
Buying Data:
- Register on the marketplace platform.
- Search for datasets using relevant keywords or filters.
- Review dataset descriptions, licensing terms, and prices.
- Purchase the data and integrate it into your systems.
Selling Data:
- Prepare and structure your data.
- Register as a seller on the platform.
- Upload datasets with detailed metadata and pricing information.
- Ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
- Manage sales and monitor performance.
Ensuring Privacy, Security, and Trust in Data Marketplaces
Privacy and security are critical concerns for data marketplaces. Key measures include:
Data Privacy: Protecting Sensitive and Personal Information
With stringent data protection laws such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), data marketplaces must implement robust privacy measures to protect users’ personal and sensitive information. Key strategies to ensure privacy include:
- Anonymization & Data Masking: Before datasets are shared or sold, they undergo de-identification, where personally identifiable information (PII) is removed or altered to prevent the identification of individuals.
- Differential Privacy: This advanced privacy technique adds statistical noise to datasets, ensuring that insights can be extracted without exposing individual user data.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Data marketplace architecture is made the way to implement access restrictions so that only authorized users can view, download, or modify data.
- Data Ownership and Consent Management: Sellers retain control over how their data is used, and individuals whose data is included must provide explicit consent before it is shared.
Security Measures to Prevent Data Breaches
The value of data makes data marketplaces a prime target for cyber threats such as hacking, fraud, and unauthorized access. To protect against these risks, robust security frameworks must be in place. They include:
- End-to-End Encryption: Data must be encrypted both at rest and in transit using industry standards like AES-256 encryption. This prevents unauthorized users from intercepting or modifying the data.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Secure login procedures, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), add an extra layer of protection, ensuring that only verified users can access sensitive datasets.
- Blockchain and Smart Contracts: Some data marketplaces like Datum or DX Network use blockchain technology to create an immutable record of transactions, preventing fraud and unauthorized modifications.
- Intrusion Detection and Threat Monitoring: AI-powered security systems can detect unusual activity, such as unauthorized access attempts, and take immediate action to mitigate threats.
- Regular Security Audits & Penetration Testing: Ethical hackers and cybersecurity teams continuously test marketplace vulnerabilities to identify and fix security loopholes before they can be exploited.
Building Trust Through Transparency and Fair Governance
For a data marketplace to thrive, it must create a trustworthy ecosystem where buyers and sellers feel confident in the quality, authenticity, and ethical sourcing of data. To achieve this, marketplaces must emphasize:
- Transparent Data Provenance: Buyers should know exactly where the data comes from, how it was collected, and whether it meets legal and ethical standards. Blockchain-based ledgers can help track data origins and ensure authenticity.
- Data Certification and Quality Ratings: Marketplaces should provide verification badges or certification labels to indicate that data has been validated by independent auditors or meets industry standards.
- Clear Licensing Agreements: Well-defined data usage policies and licensing agreements prevent misunderstandings about how data can be used, shared, or resold.
- Reputation Systems and User Feedback: Allowing buyers to rate and review datasets fosters transparency and encourages sellers to maintain high-quality offerings.
Key Requirements for a Successful Data Marketplace
To thrive, a data marketplace must meet these criteria:
High-Quality and Well-Structured Data
The success of a data marketplace hinges on the quality, accuracy, and relevance of the data being offered. Buyers need reliable datasets that provide meaningful insights, and sellers must ensure their data meets industry standards. Key aspects:
- Accuracy & Completeness: The data should be up-to-date, free from errors, and complete, with minimal missing values.
- Standardized Formats: Data should be structured in common formats (e.g., CSV, JSON, XML, Parquet) to ensure easy integration with various systems.
- Metadata & Documentation: Each dataset should include detailed metadata, explaining its source, methodology, collection date, and intended use cases.
- Validation & Certification: Trusted third-party certifications or marketplace-verified data can help ensure buyers receive high-quality datasets.
- Update & Refresh Mechanisms: Marketplaces should offer real-time or scheduled updates, ensuring that datasets remain relevant over time.
Scalable Infrastructure & Performance Optimization
A successful data marketplace must handle large volumes of data transactions efficiently. This requires a scalable, high-performance infrastructure that can support:
- Large-Scale Data Storage & Management: The marketplace must handle terabytes or petabytes of structured and unstructured data. Cloud-based storage solutions (e.g., AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage) enable seamless scaling.
- High-Speed Data Processing: Real-time or near-real-time data access improves user experience. Technologies like Apache Kafka, Snowflake, and BigQuery can enhance data processing speeds.
- API Integrations: A marketplace should offer RESTful APIs or GraphQL endpoints, allowing businesses to automate data retrieval and integration.
- Global Accessibility & Load Balancing: Ensuring data availability across regions with CDN (Content Delivery Networks) and multi-region deployments improves performance for users worldwide.
- Redundancy & Failover Mechanisms: Implementing backup strategies and failover systems minimizes downtime and ensures continuous data availability.
Intuitive User Experience (UX) & Seamless Navigation
Even the most powerful data marketplace will struggle if it lacks usability. A user-friendly interface with intuitive navigation improves engagement and transaction success rates. Key UX features include:
- Advanced Search & Filtering: Users should be able to filter datasets based on keywords, industry, data format, licensing terms, and pricing models.
- Dataset Previews & Samples: Offering data previews or sample datasets allows buyers to assess quality before purchasing.
- Interactive Dashboards: Providing visual insights, analytics, and trend tracking can enhance decision-making for buyers.
- Easy Checkout & Licensing Management: A streamlined purchase process with clear licensing options ensures a smooth transaction experience.
- Mobile-Friendly Design: A responsive interface that works across desktop, tablet, and mobile devices increases accessibility.
- A well-designed marketplace reduces friction, making it easier for buyers to find and purchase relevant datasets.
Trust and Reputation Management
For a data marketplace to succeed, trust must be a central pillar. Buyers need confidence that they are purchasing accurate, legal, and ethically sourced data, while sellers need assurance that transactions are secure and fairly compensated. Ways to build trust in a data marketplace:
- Reputation & Rating System: Allowing users to rate and review datasets based on quality, accuracy, and value.
- Verified Sellers & Buyers: Implementing an ID verification service and certification badges helps highlight reputable providers. This added layer of trust ensures that only genuine sellers and buyers engage on the platform, improving safety and credibility for all users.
- Transparent Data Provenance: Ensuring datasets have clear origin tracking and verifiable sources.
- Clear Refund & Dispute Resolution Policies: Establishing buyer protection policies in case of data discrepancies or fraud.
- Community & Support Services: Offering a customer support team, community forums, and documentation to assist users.
- Trust mechanisms reduce fraudulent activities, enhance buyer confidence, and encourage long-term marketplace growth.
How to Build Your Data Marketplace?
Formulate Your Strategy
A key step is to align your data market plans with your organization’s business goals and processes. Consider data as a strategic asset that will help your collateralized debt obligations demonstrate their business value. Also consider operational costs and data quality to help manage regulatory risks in the future.
Define the Pilot Project and Launch MVP
You can start with a straightforward strategic scenario of launching a marketplace that can deliver quick and visible results. Selecting the right assets to launch a pilot is your primary objective. You will also need to evaluate and partner with data providers.
Next, a great solution is to launch an MVP project that allows you to test business hypotheses and identify user needs with minimal cost and risk. With an out-of-the-box platform like CS-Cart Multi-Vendor, you can get an MVP up and running in no time.
Prepare Data Assets
Your user community should have easy access to your data. Implement access controls for protection and document provisions for general use and restrictions. Your platform should be GDPR compliant, ensuring data security and privacy.
The best solution is to automate the data submission path. Also, consider scalability to ensure the success of not only a pilot launch, but also the continued growth of the platform.
Since a data marketplace involves working with a colossal amount of data, you may want to consider using VPS and cloud hosting for eCommerce platforms, like Scalesta. Optimized servers, configured to your business needs, provide: performance and security monitoring, daily backups and fast response to incidents according to SLA. At the same time, a point-in-time capacity increase based on real load allows you to scale without the obstacles of architectural limitations.
Introduce Stakeholders to Your Data Marketplace
Educate and provide all necessary resources to stakeholders on your platform. Stakeholders should be trained and aware of the rules of data trading on your platform.
If you are working with an out-of-the-box solution from CS-Cart, it provides all the necessary features to manage stakeholder roles and capabilities on your marketplace. You regulate administrative access levels by assigning specific functions to them. This way, your employees can perform their tasks and your stakeholders can see the data turnover independently within one administrative dashboard.
Track Data Quality Feedback
The main goal of this step is to continuously track and monitor how data is being used in the marketplace. Gathering feedback from users is critical to understanding the performance of data products and the market as a whole, and to ensuring data quality through this continuous feedback process. Maintaining high standards of data quality is necessary to make informed adjustments and improvements to ensure that the market meets user needs and business objectives.
Refine Your Data Marketplace
Analyze operational processes, data quality, user engagement, and results to continuously improve marketplace features and capabilities. The goal is to better serve the business and its customers.
Now, the data exchange business is on a journey to democratize the way data is handled, as evidenced by the following marketplace modernization milestones:
- Data Product Interoperability. Allows data providers to decide what data can be made available. The interface provides rich search capabilities that allow stakeholders to search for keywords, business terms, and natural language. It can support data discovery, glossary, and data classification.
- Data Tier Distribution. Helps automate the deployment and configuration of consumption templates that are generic and reusable. Consumption templates can include storage accounts, databases, compute, credential management, etc.
- Implement Automated Monitoring. Monitors the health status of all interfaces, data pipelines, data contracts, provisioned components, central tools, etc.
Closing
Data marketplaces are reshaping how businesses access and utilize information, driving innovation and economic growth. Platforms like Snowflake Data Marketplace and AWS Data Marketplace demonstrate the potential of a well-structured, secure, and scalable data marketplace platform. As industries continue to rely on data for competitive advantage, the importance of these platforms will only grow, making them a cornerstone of the modern digital economy.
And if you need expert advice on fine-tuning your data marketplace? Simtech Development is here to help!
FAQ
1. How Data Marketplaces Enable Data Monetization?
Data marketplaces allow businesses and individuals to sell data through one-time purchases, subscriptions, or pay-per-use models. Blockchain-based platforms like Ocean Protocol enhance security and automate payments with smart contracts.
2. What Is the Difference Between Internal and External Data Marketplaces?
Internal Data Marketplaces – Used within an organization to facilitate secure data sharing between departments, subsidiaries, or teams. These platforms streamline data governance, improve collaboration, and prevent data silos.
External Data Marketplaces – Open platforms where third parties can buy and sell data. These marketplaces enable businesses to acquire datasets from diverse sources, including commercial vendors, government agencies, and individuals.
3. Who Are the Key Players in the Data Marketplace Ecosystem?
Several stakeholders contribute to the data marketplace ecosystem:
- Data Providers – Organizations, businesses, and individuals who generate and sell data.
- Data Buyers – Companies, AI developers, and researchers who purchase data for analytics, machine learning, and business insights.
- Marketplace Operators – Platforms that facilitate data transactions, ensure compliance, and provide infrastructure for secure data exchange (e.g., Snowflake Data Marketplace, Oracle Data Marketplace, Ocean Protocol).
- Regulatory Bodies – Government agencies and industry organizations that establish data privacy and compliance regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Technology Enablers – Companies providing blockchain, AI, and cloud computing solutions.

