Multi-vendor marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, and Alibaba have seen significant growth and have become generic names in the eCommerce industry. They offer a wide range of products from various sellers, making it convenient for customers to compare options and find competitive prices.
According to a study by Digital Commerce 360, in 2022, 68% of global online shoppers made their product purchase on Amazon.
This indicates the popularity and dominance of marketplaces in certain regions. If you want to replicate the success of the above multi-vendors, this article is for you. Find answers on the marketplace building steps, key features, software solutions, and revenue models.
What is a multi-vendor marketplace?
Example of a multi-vendor marketplace that promotes its services with sellers
A multi-vendor marketplace is an online platform where multiple sellers come together to sell their products and services to customers. It allows different vendors to create their own stores within the marketplace and manage their inventory, pricing, and orders independently.
In a multi-vendor marketplace, customers can browse through various items from different sellers, compare prices, and make purchases from multiple vendors in a single transaction. The marketplace operator typically handles the payment and order processing.
How does multi-vendor marketplace platform work?
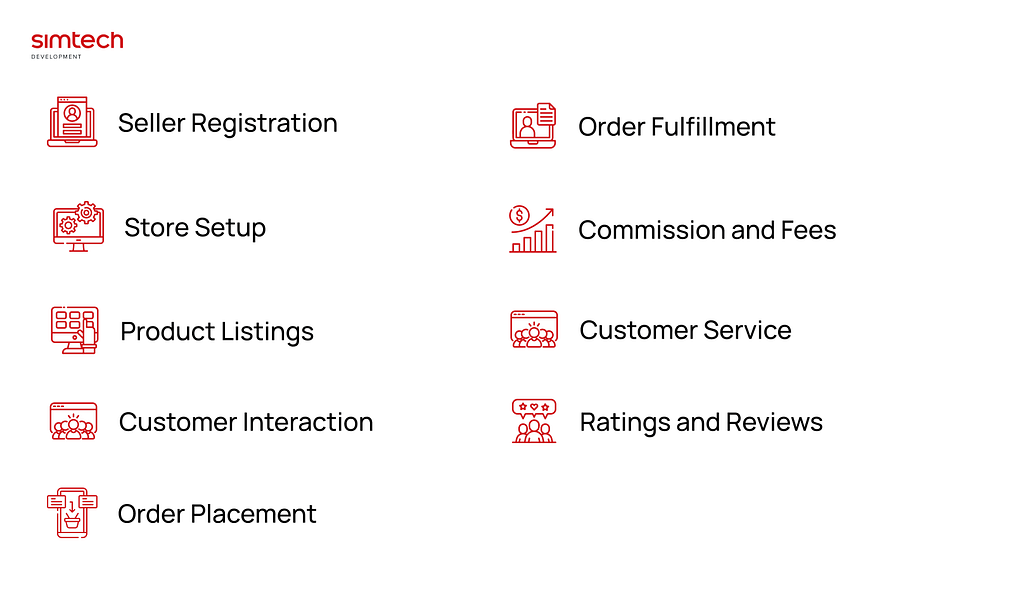
A multi-vendor provides a centralized online platform for sellers and typically works as follows:
- Seller Registration: Sellers register on the marketplace platform and create their own vendor accounts. They provide their contact details, product/service listings, pricing, and shipping options.
- Store Setup: Sellers set up their individual stores within the marketplace platform. They customize their store appearance, upload product images, write descriptions, and manage their inventory.
- Product Listings: Vendors list their inventory in their respective stores. They provide details such as product name, description, price, variants (if applicable), and other relevant information for the product cards.
- Customer Interaction: Customers visit the marketplace platform and browse through different sellers’ stores. They can search for specific products, filter by categories, read product descriptions, view images, and compare prices.
- Order Placement: When customers find a product they want to purchase, they add it to their cart and proceed to checkout. The marketplace platform handles the payment processing, allowing customers to make a single payment for products from multiple sellers.
- Order Fulfillment: Once an order is placed, the multivendor marketplace platform notifies the respective sellers. Sellers are responsible for packaging and shipping their products to the customers. They update the order status and provide tracking information through the platform.
- Commission and Fees: The marketplace platform typically charges a commission or fee for facilitating the transactions. This can be a percentage of each sale or a fixed fee. Sellers receive their payments after deducting the platform’s commission.
- Customer Service: The marketplace platform often provides customer care service to handle inquiries, disputes, and returns. They act as an intermediary between customers and sellers to ensure a smooth buying experience.
- Ratings and Reviews: Customers can leave ratings and reviews for products and sellers, helping other buyers make informed decisions. This feedback system encourages sellers to maintain quality and customer satisfaction.
To summarize, a multi-vendor marketplace platform acts as a facilitator, connecting sellers and buyers, managing transactions, and providing a secure and convenient shopping experience for customers.

Save time and budget with our Multi-Vendor Marketplace Development services
Advantages of the multi-vendor eCommerce marketplaces
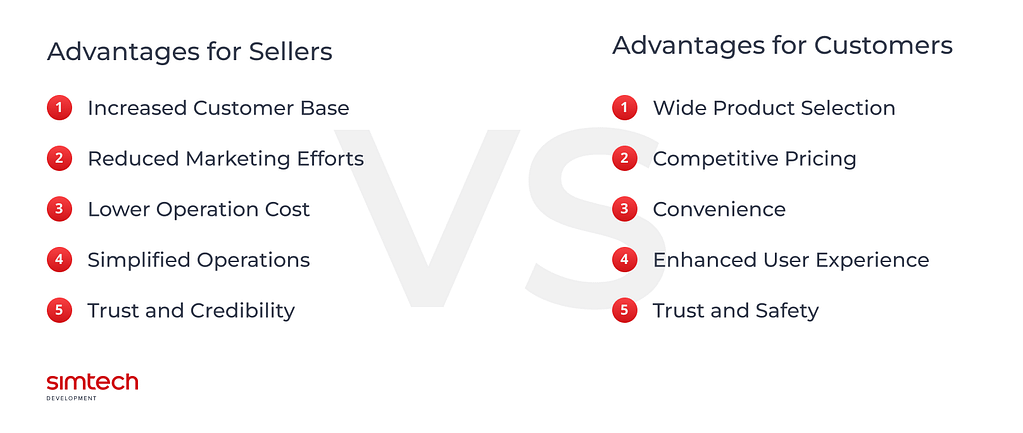
Let’s see key advantages of multi-vendor marketplaces:
Advantages for Sellers
- Increased Customer Base: Sellers leverage the existing customer base and traffic of the marketplace multi vendor platform to reach a larger audience. This exposure helps them gain visibility and attract potential customers who might not have discovered their individual stores.
- Reduced Marketing Efforts: Vendors benefit from the marketing efforts and promotional activities carried out by the marketplace platform. They can take advantage of the platform’s branding, advertising, and customer acquisition strategies, saving them time and resources on individual marketing campaigns.
- Lower Operating Cost: Setting up and maintaining an individual online store is costly. By joining a multi-vendor marketplace, sellers avoid expenses like website development, hosting, and payment gateway integration. They can focus on product creation and fulfillment instead.
- Simplified Operations: The marketplace platform handles various aspects of operations, such as payment processing, order management, and customer support. Sellers save time and effort by relying on the platform’s infrastructure and tools.
- Trust and Credibility: Established multivendor marketplace platforms often have a reputation for trust and credibility among customers. Customers are more likely to make purchases from a known and reliable platform.
Advantages for Customers
- Wide Product Selection: Customers have access to a diverse range of products and services from multiple sellers in one place. They easily compare options, read reviews, and make informed purchasing decisions.
- Competitive Pricing: With multiple sellers competing on the same platform, customers often find competitive prices and deals. Sellers may offer discounts and promotions to attract customers, resulting in cost savings for buyers.
- Convenience: Customers shop from multiple brands and add products from different stores to a single cart. This eliminates the need to visit multiple websites and make separate transactions, saving time and effort.
- Enhanced User Experience: Multi-vendor marketplaces often provide user-friendly interfaces, advanced search and filtering options, and personalized recommendations. These features improve the overall shopping experience for customers.
- Trust and Safety: Established marketplaces usually have measures in place to ensure secure transactions, protect customer data, and handle disputes. Customers feel more confident about their purchases and have recourse if any issues arise.
In other words, multi-vendor eCommerce marketplaces are a win-win solution for both sellers and customers. Vendors reach a wider audience, reduce costs, and simplify operations, while customers benefit from a wide selection, competitive pricing, convenience, and trustworthiness of the platform.
Multi-vendor marketplace types
There are different types of multi-vendor ecommerce websites, each catering to specific industries or business models. The most common types include:
- General Merchandise Marketplaces: These are multi-vendor marketplaces that offer a wide range of products across various categories. Examples include Amazon, eBay, and Walmart Marketplace.
- Niche Marketplaces: These marketplaces focus on specific industries or product categories. For instance, Etsy is a niche marketplace for handmade and vintage items, while Houzz is a marketplace for home decor and furniture.
- Service Marketplaces: Instead of physical products, these marketplaces connect customers with service providers. Examples include Upwork for freelancers, Airbnb for accommodations, Steam Marketplace for video game items. and Uber for transportation services.
- Rental Marketplaces: These marketplaces allow individuals or businesses to rent out their assets or services. Examples include Airbnb for short-term rentals, Turo for car rentals, and Rent the Runway for clothing rentals.
- Local Marketplaces: These marketplaces focus on facilitating transactions within a specific geographic area. They connect local sellers with local customers, promoting community-based commerce. Examples include Craigslist and Facebook Marketplace.
- Digital Goods Marketplaces: These marketplaces specialize in selling digital items such as software, e-books, music, and online courses. Examples include iTunes, Google Play Store, and Udemy.
- Crowdfunding Platforms: These platforms allow individuals or businesses to raise funds for their projects or ideas. Examples include Kickstarter, Indiegogo, and GoFundMe.
These are just a few examples of multi-vendor marketplace types, and there are many more variations based on specific industries, business models, and target audiences. The type of marketplace chosen depends on the specific needs and goals of the sellers and customers involved.
How to Create a Multi-Vendor Marketplace Website?
Creating a multi-vendor website involves several steps. Here’s a general outline of building a multi-vendor marketplace from scratch.
Define Your Marketplace Concept
Determine the niche or industry you want to target, your future customer profile, the types of products or services you want to offer, and the unique selling proposal of your marketplace. Don’t forget to conduct competitor analysis to make your offer more appealing for prospects.
Choose a Platform
Select an optimal platform to build your marketplace website. You can choose from options like WooCommerce with extensions, Magento with marketplace add ons, Shopify with multi-vendor apps, or dedicated marketplace software like Sharetribe or CS-Cart.
Set Up the Website
Install and configure the chosen platform on your web hosting server. For an MVP version, simple setup and integrations out of the box will be enough. For more complex projects, it may require more modifications, custom design, etc. Customize the design and layout of your website to align with your branding and user experience goals.
Enable Multi-Vendor Functionality
Install and configure the necessary plugins, extensions, or apps to enable multi-vendor functionality on your chosen platform. Note that in CS-Cart the multi-vendor feature is provided by default. Find the installation guide here. Alternatively, you can build the marketplace website from scratch. You will need to define the appropriate programming language for the development and find a reliable IT agency to perform this work.
Establish Seller Registration and Onboarding
Create a seller registration process where sellers can sign up, provide necessary information, and get approved to start selling on your marketplace. Develop onboarding materials or tutorials to help sellers understand how to use the platform effectively. Learn how to reduce setup friction and help vendors start selling faster with a structured marketplace seller onboarding process.
Implement Payment, Shipping and Commission System
Set up a payment gateway to handle transactions between buyers and sellers and shipping systems – to deliver items fast and easy. Create a commission structure to determine the fees or percentages you will charge sellers for each transaction or listing.
Develop Seller Management Tools
Build a dashboard or interface for sellers to manage their products, inventory, orders, and customer communications. Provide tools and analytics to help sellers track their performance, sales, and customer feedback.
Launch and Market Your Marketplace
Once your website is ready, launch your marketplace and start marketing it to attract sellers and buyers. Utilize various marketing channels, such as social media, content marketing, influencer partnerships, and paid advertising, to promote your marketplace.
Monitor and Optimize
Continuously monitor the performance of your marketplace, gather feedback from users, and make necessary improvements and optimizations to enhance the user experience, attract more sellers, and increase customer satisfaction.
Remember that creating a multi-vendor eCommerce platform is a complex process that requires technical expertise, careful planning, and ongoing maintenance. Consider seeking professional help or utilizing pre-built marketplace platforms if you’re not familiar with web development or the intricacies of running a marketplace.
Key Features List of Multi-Seller Marketplace Platform
A multi-seller marketplace platform should have several key features to facilitate smooth transactions between sellers and buyers. Consider the following important features to add:
User Registration and Profiles
Amazon allows creating a seller account with mobile phone or email
Allow sellers and buyers to create accounts and manage their profiles. Sellers should be able to provide necessary information, such as contact details, product descriptions, and shipping policies. Don’t forget to simplify this process to ease onboarding of sellers and encourage more guest visitors to convert into buyers.
Product Listing and Management
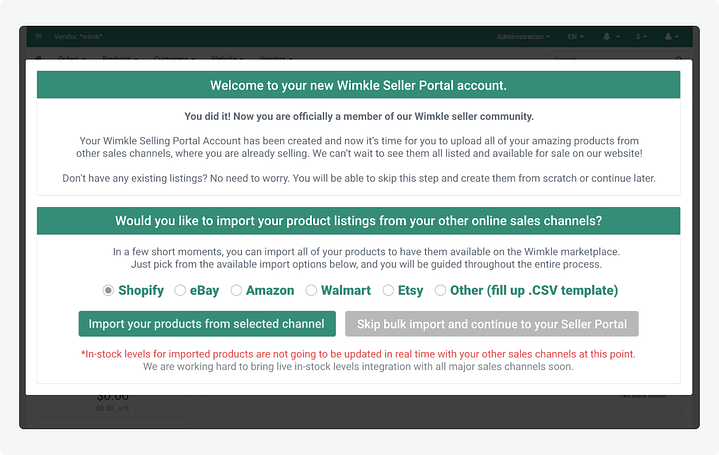
Some marketplaces allow vendors to upload their inventory from other platforms
Enable vendors to easily list and manage their goods or services. This includes features like adding product descriptions, images, pricing, inventory management, and the ability to edit or deactivate listings.
Order and Payment Processing
Provide a streamlined process for buyers to add products to their cart, proceed to checkout, and make payments securely. To boost conversions, add product tours that walk new vendors through listing and managing their first products—these guided walkthroughs can significantly reduce setup friction and improve onboarding success. The platform should support various payment gateways and offer secure transaction processing.

Cryptocurrency is the new trend in payment options
Commission and Fee Management
Implement a commission or fee structure to charge sellers for each transaction. The platform should calculate and track these fees automatically, providing transparent reporting and payment settlement.
Messaging and Communication
Enable direct communication between buyers and sellers through a messaging system. This allows them to ask questions, negotiate terms, and resolve any issues or concerns.
Seller Analytics and Reports
Offer comprehensive analytics and reporting tools for sellers to track their sales, performance, and customer behavior. This data helps sellers make informed business decisions and optimize their offerings.
Mobile-Friendly Design
Ensure that the marketplace platform is responsive and mobile-friendly, allowing users to access and use the platform seamlessly on various devices.
Dispute Resolution
Provide customer support channels to address inquiries, issues, or disputes that may arise between buyers and sellers. This can include email support, live chat, or a dedicated support ticketing system.
Social Sharing and Integration
Enable social sharing features to allow users to share products or services on social media platforms, increasing visibility and reach. Integration with social media accounts and other marketing tools can also be beneficial.
Customization and Branding
Offer customization options to allow marketplace owners to align the platform with their branding and design preferences. This includes customizable themes, colors, logos, and other visual elements.
These are some essential features for a multiseller marketplace platform. The specific features needed may vary depending on the industry, target audience, and unique requirements of your marketplace.
Software Solutions for Multi-vendor marketplace development
As we have already mentioned, there are several multi-vendor marketplace software solutions on the market. Here are some popular options:
Adobe Commerce (former Magento)

Adobe Commerce is a robust and scalable eCommerce system that offers a multi-vendor marketplace extension for marketplaces. It provides features like vendor registration, product listing, order processing, commission management, and more.
WooCommerce

WooCommerce is a popular WordPress plugin that can be extended to create a multi-vendor marketplace using plugins like “WooCommerce Product Vendors” or “Dokan.” It offers features such as vendor registration, inventory management, order processing, commission tracking, and more. With external integrations, vendors can sync WooCommerce orders to Google Sheets for simplified reporting and data analysis
Shopify

Shopify is a widely-used hosted eCommerce software that offers multi-vendor functionality through apps like “Multi Vendor Marketplace” or “Webkul Marketplace.” These apps allow sellers to create profiles, list products, manage inventory, process orders, and handle payments.
OpenCart

OpenCart is an open-source eCommerce platform that can be extended with modules like “MultiMerch” or “Webkul Multi-Vendor Marketplace” to create a multi-vendor marketplace. It offers features such as vendor registration, product listing, order management, commission tracking, and more.
Yo!Kart

Yo!Kart is a dedicated multi-vendor marketplace solution that offers a range of features for building and managing a marketplace. It includes features like vendor registration, product management, order processing, commission tracking, vendor analytics, and more.
Sharetribe

Sharetribe is a platform specifically designed for creating peer-to-peer marketplaces. It offers features like vendor registration, product listing, order management, commission tracking, and a user-friendly interface for both buyers and sellers.
CS-Cart Multi-Vendor

CS-Cart is a comprehensive eCommerce solution that includes built-in multi-vendor functionality. It provides features like vendor registration, inventory management, seller analytics, order processing, commission tracking, and a user-friendly vendor dashboard.
Each platform has its own set of features, pricing, and customization options, so it’s important to evaluate your specific requirements before choosing the right solution for your marketplace.
Revenue Structure of Multi-Vendor eCommerce Marketplace Owners
In a multi-vendor, the marketplace owner acts as a facilitator or intermediary between the sellers and buyers. The marketplace owner provides the platform, infrastructure, and tools for sellers to list and manage their products, while also offering a seamless shopping experience for buyers.
The owner typically earns revenue through various revenue streams, such as:
- Commission Fees: The marketplace founder charges a commission fee or a percentage of each transaction made on the platform. This fee is usually based on the total order value or the product price. The commission fee can vary depending on the product (service) category, seller performance, or other factors.
- Subscription Fees: The owner may offer different subscription plans for sellers, allowing them to access additional features or benefits. Sellers pay a monthly or annual subscription fee to avail these premium services.
- Listing Fees: The marketplace owner may charge sellers a fee for listing on the platform. This fee can be a one-time fee or a recurring fee for each listing.
- Advertising and Promotional Fees: The multi-vendor owner may offer advertising or promotional opportunities for sellers to increase their visibility on the platform. Sellers can pay a fee to feature their products in prominent positions or run targeted advertising campaigns.
- Transaction Fees: The owner may charge a flat fee or a percentage of the transaction value for each successful transaction made on the platform. This fee covers the cost of payment processing and transaction management.
- Additional Services: The marketplace owner may offer additional services to sellers, such as logistics, warehousing, or fulfillment. These services can be charged separately, either as a one-time fee or on a recurring basis.
The revenue structure varies depending on the specific business model, industry, and target market. It’s important for marketplace owners to carefully consider their revenue streams and pricing strategies to ensure profitability while providing value to both sellers and buyers.
Challenges of building the successful multi-seller marketplace

Building a successful multi-seller marketplace can be a complex and challenging endeavor. Be aware of some common challenges:
Attracting Sellers
One of the biggest challenges is attracting a sufficient number of quality sellers to the marketplace. Sellers may hesitate to join a new marketplace with limited visibility and customer base. Building trust and offering incentives can help overcome this challenge. Read an inspiring story of our client to learn how they overcame this challenge.
Ensuring Product Quality and Consistency
Maintaining product quality and consistency across multiple sellers can be a challenge. Implementing strict seller onboarding processes, quality control measures, and customer feedback systems can help address this challenge.
Managing Seller Relationships
Managing relationships with multiple sellers can be time-consuming and requires effective communication and support. Providing clear guidelines, offering seller support, and addressing seller concerns promptly can help build strong relationships.
Balancing Supply and Demand
Balancing the supply of products or services with customer demand is crucial for a successful marketplace. Ensuring that there are enough sellers and products to meet customer demand, especially during peak periods, can be challenging.
Ensuring Competitive Pricing
Maintaining competitive pricing across multiple sellers can be challenging. Implementing pricing guidelines, monitoring market trends, and offering tools for sellers to optimize their pricing can help address this challenge.
Managing Logistics and Fulfillment
Logistics and fulfillment can be complex when multiple sellers are involved. Implementing efficient shipping and fulfillment processes, providing tracking information, and ensuring timely delivery can help provide a positive customer experience.
Ensuring a Seamless User Experience
Providing a seamless and user-friendly experience for both sellers and buyers is essential. Investing in a well-designed and intuitive platform, offering comprehensive search and filtering options, and providing responsive customer care can help enhance the user experience.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, effective execution, and continuous improvement. It’s important for marketplace owners to understand their target market, differentiate their platform, and provide value to both sellers and buyers to build a successful multi-seller marketplace.
High Load
A high-load online marketplace needs to handle a large volume of traffic, transactions, and user interactions without experiencing performance issues or downtime. Consider the following features with your hosting provider:
- Scalability: The platform should be built with scalability in mind, allowing it to handle increasing traffic and user demands. This can be achieved through technologies like cloud hosting, load balancing, and horizontal scaling.
- Performance Optimization: The marketplace should be optimized for fast page load and efficient database queries. Techniques like caching, content delivery networks (CDNs), and database indexing can help improve performance.
- Robust Infrastructure: A high-load marketplace requires a robust infrastructure with redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure high availability. This may involve multiple servers, load balancers, and backup systems.
- Database Management: Efficient database management is crucial for handling high loads. Implementing techniques like database sharing, replication, and caching can help distribute the load and improve database performance.
- Caching and Content Delivery: Utilizing caching mechanisms and content delivery networks (CDNs) can help reduce the load on the server and improve the delivery of static content like images and CSS files.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Implementing monitoring tools and analytics systems can help track the performance of the marketplace, identify bottlenecks, and optimize the platform for better performance.
- Security: A high-load marketplace should have robust security measures in place to protect user data, prevent fraud, and ensure secure transactions. This may involve implementing SSL encryption, secure payment gateways, and regular security audits.
It’s crucial to consult with experienced developers and infrastructure specialists to ensure that the chosen platform and architecture can handle the expected load and provide a seamless user experience even during peak times, which is essential for growing your multi-vendor marketplace..
How Much Does It Cost To Build a Multi-Vendor Marketplace?
The cost of building a multi-vendor marketplace can vary significantly depending on various factors such as the complexity of the platform, the features and functionalities required, the technology stack chosen, the level of customization, and the development approach (in-house development or outsourcing).
Here are some cost components to consider when estimating the cost of building a multi-vendor marketplace:
- Platform Development: The development of the marketplace platform itself is a significant cost component. This includes front-end and back-end development, database design, user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design, and integration of various features and functionalities. The cost can vary depending on the complexity of the platform and the technology stack chosen.
- Customization and Branding: If you require customizations and branding specific to your marketplace, such as unique design elements, custom features, or integration with third-party systems, it may add to the development cost.
- Mobile App Development: If you plan to have a mobile application for your marketplace, the cost of developing native or hybrid mobile apps for iOS and Android platforms should be considered separately.
- Payment Gateway Integration: Integrating payment gateways to facilitate secure transactions on your marketplace may involve additional costs, including setup fees, transaction fees, and ongoing maintenance fees.
- Hosting and Infrastructure: The cost of hosting and infrastructure depends on the scale and expected traffic of your marketplace. It includes the cost of servers, cloud hosting services, content delivery networks (CDNs), and security measures.
- Third-Party Integrations: If you plan to integrate third-party services, such as shipping providers, analytics tools, or marketing automation platforms, there may be additional costs associated with integration and ongoing usage.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: It is essential to allocate a budget for thorough testing and quality assurance to ensure the functionality, performance, and security of your marketplace.
- Maintenance and Support: Ongoing maintenance, bug fixes, feature enhancements, and technical support should be considered as part of the overall cost. This can be done in-house or outsourced to a development team.
Our Multi-Vendor Marketplace Examples
SeeWhatHappens

- Segment: B2C
- Category: Glasses, beauty and personal care
- Type: marketplace from scratch
- Main business goal: make design changes and integrate systems for better user experience
Key functions:
This optical marketplace offers an opportunity to find the nearest optician, enter a prescription, book an appointment with a local optician, and even virtually try on glasses
Project goals:
- Integrate a service for glasses virtual try-on
- Introduce a feature to find the nearest optician
- Add an opportunity to book an appointment with a local optician
- Develop a functionality to enter a prescription
- Configure and release Stripe Connect
Gemsquar
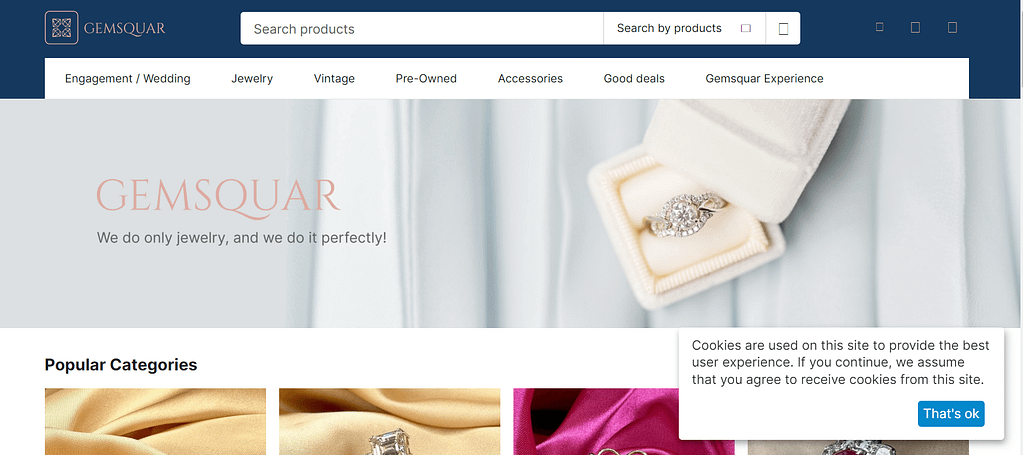
- Segment: B2C
- Category: jewelry, Beauty and personal care
- Type: marketplace
- Main business goal: make design changes to better serve customers
Key features:
Jewelry marketplace with unique design, the size guide, calendar, and tags block.
Project goals:
- Create a jewelry marketplace from scratch based on the standard license
- Redesign the store to add Calendar, Size guide and other options to better serve customers
Unixmo

- Segment: B2C, B2B
- Category: car, car parts
- Type: marketplace
- Main business goal: introduce affiliate program to offer discounts for members
Key functions:
An automotive marketplace from Australia with an affiliate program and ability to sustain high loads
Project goals:
- Master a new market (target audience – residents of neighboring Australia, individuals and legal entities), focus on increasing the number of suppliers of goods and services.
- Promote the partnership program between UNIXMO and the New Zealand Automotive Repair Industry Society “Capricorn” (a 50-year-old association helping SMEs in the automotive industry grow their businesses, 11,000 members, 4,500 companies, over 50 support programs for business owners).
- Implement a system of automatic payments, including the return of goods.
- Get an optimal hosting solution to improve marketplace performance.
These are just a few examples of the customization services offered by Simtech Development. We have a team of experienced developers who can tailor the multi-vendor marketplace platform to your specific needs and requirements.

